Tolerance Control in Injection Molding: Definition, Key Technologies, Applications, and China Supplier Insights
Keyword: Tolerance control in injection molding
Word Count Target: ~3000 words
Introduction
Injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing methods for producing complex plastic parts with high precision and repeatability. Within this highly refined process, tolerance control in injection molding plays a critical role in determining product quality, performance, and assembly compatibility.
For engineers, product designers, and manufacturers, understanding how to manage and specify tolerances in injection molding can significantly impact cost, function, and production efficiency. China, as the global hub for plastic manufacturing, offers a wide range of suppliers and manufacturers with advanced tolerance control capabilities, making it a crucial destination for sourcing precision plastic parts.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore:
- The definition and importance of tolerance control
- Key technologies enabling tight tolerance control
- Industry applications requiring high tolerance standards
- The Chinese supplier landscape
- Best practices for specifying and working with tolerance-sensitive parts
What is Tolerance Control in Injection Molding?
Definition
Tolerance control in injection molding refers to the allowable deviation in a dimension of a molded plastic part from its nominal value. It is expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.02 mm) and defines the upper and lower limits for acceptable part dimensions.
Why Tolerances Matter
- Fit and Function: Components must fit with mating parts precisely.
- Assembly Efficiency: Tight tolerances reduce the need for post-processing.
- Product Reliability: Minimizes failure due to misalignment or stress concentration.
- Cost Optimization: Looser tolerances reduce manufacturing costs, but compromise on precision may increase risk.
Types of Tolerances in Injection Molding
- Dimensional Tolerance
The deviation in part dimensions such as length, width, height, or diameter. - Geometric Tolerance
Defines shape, profile, orientation, or location (e.g., flatness, perpendicularity). - Shrinkage Tolerance
Accounts for plastic shrinkage during cooling; critical during mold design. - Positional Tolerance
Ensures correct positioning of holes, slots, and other features. - Surface Tolerance
Tolerances related to the texture or finish of the surface.
Industry Standards for Tolerance Control
Common tolerance standards include:
- ISO 20457 (Plastics — Molded Parts — Tolerances)
- DIN 16901 (German Standard for Injection Molded Parts)
- SPI Guidelines (U.S. Society of Plastics Industry)
Standard classes include:
| Class | Description | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Fine | ±0.01 to ±0.05 mm | Medical, optics, electronics |
| Medium | ±0.1 to ±0.3 mm | Consumer goods, automotive |
| Coarse | ±0.3 mm and above | Toys, general plastics |
Key Technologies for Tolerance Control
1. High-Precision Tooling
- Mold cavities are CNC-machined with micrometer-level accuracy.
- Tool steels with low thermal expansion used to maintain dimensional consistency.
2. Scientific Molding Techniques
- Use of real-time monitoring and closed-loop control.
- Parameters like fill time, injection speed, pressure, and hold time are optimized.
3. Material Selection
- Plastics like POM, PEEK, PC, and PPS have lower shrinkage variability.
- Fillers (glass, carbon) reduce distortion.
4. In-Mold Sensors & IoT Monitoring
- Sensors monitor pressure, temperature, and flow in real-time.
- Helps maintain consistent part dimensions from shot to shot.
5. Post-Molding Techniques
- Annealing or conditioning to stabilize dimensions.
- Precision machining (if tolerances cannot be achieved in-mold).
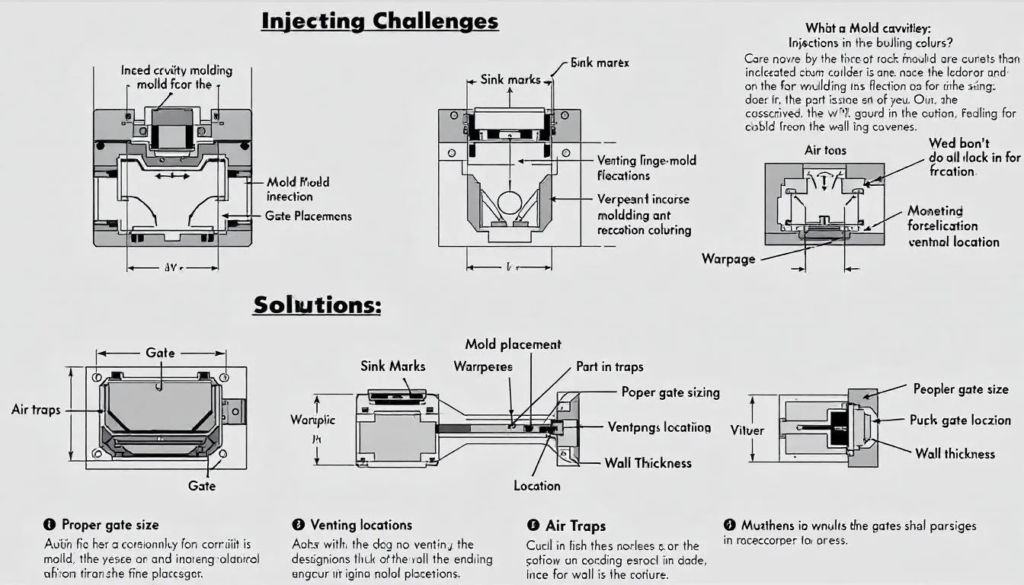
Challenges in Tolerance Control
- Material Shrinkage: Each plastic has a unique shrink rate; managing this is essential.
- Warping and Distortion: Uneven cooling or fiber orientation can lead to warping.
- Environmental Factors: Humidity, temperature changes post-molding.
- Complex Geometries: Tight tolerances harder to maintain in deep ribs, thin walls.
Applications That Require Tight Tolerance Control
- Medical Devices
- Surgical instruments, inhalers, diagnostic components
- Requires ISO 13485 certified facilities
- Automotive Components
- Sensors, lighting housings, connectors
- Must meet PPAP, IATF 16949 requirements
- Electronics and Semiconductors
- Housings for PCBs, connectors, battery compartments
- Demands precision down to 0.01 mm
- Aerospace and Defense
- Lightweight, reliable components for critical operations
- Optics and Lenses
- Transparent parts must be dimensionally accurate and distortion-free
Tolerance Control in Chinese Injection Molding Facilities
China has become a global powerhouse in high-precision plastic injection molding. Here’s why:
Advantages of Chinese Suppliers
- Advanced Tooling Infrastructure: WEDM, 5-axis CNC, CMM for inspection
- Experience with Export Markets: Compliance with EU and U.S. standards
- Cost-Effective Production: Competitive labor and raw material prices
- One-Stop Solutions: Design, DFM, mold making, molding, post-processing
Key Manufacturing Hubs
| Region | Strengths |
| Dongguan, Guangdong | High-precision electronics, medical molding |
| Shenzhen | Prototypes, tooling, rapid injection |
| Suzhou, Jiangsu | Automotive and industrial parts |
| Ningbo, Zhejiang | Export-oriented factories, diverse plastic parts |
| Taizhou, Zhejiang | Mold making capital, extensive experience |
Top Chinese Suppliers Specializing in Tolerance Control
| Company | Location | Core Capability | Certifications |
| GOTOMOLD | Dongguan | Rapid tooling, tight tolerance medical & auto parts | ISO9001, ISO13485 |
| DJ Mold | Shenzhen | Prototyping, 0.01mm tolerance molding | ISO9001, IATF16949 |
| Abery Mold | Shenzhen | Mold flow analysis + insert molding precision | CE, RoHS |
| Jason Mould | Zhongshan | Precision tooling, PPAP support for auto | TS16949, ISO14001 |
| Wintech | Suzhou | High-end industrial applications | ISO9001, REACH |
Best Practices for Specifying Tolerances
- Collaborate Early: Involve suppliers during DFM stages.
- Avoid Over-Specification: Tight tolerances increase costs and defect rates.
- Account for Shrinkage: Provide CAD files and material data sheets.
- Use GD&T Where Applicable: Clearly define geometric tolerances.
- Request First Article Inspection (FAI): Validate against your drawings.
- Communicate Critical Features: Not all dimensions need the same precision.
Cost Implications of Tolerance Control
| Tolerance Level | Tooling Cost | Part Cost | Risk of Rejection |
| Loose (±0.5 mm) | Low | Low | Low |
| Medium (±0.2 mm) | Moderate | Moderate | Medium |
| Tight (±0.05 mm) | High | High | High |
Balance is key: specify the tightest tolerances only where absolutely necessary.
Summary
Tolerance control in injection molding is a critical factor that affects part quality, assembly, and performance. From material selection to tooling and process parameters, managing tolerances requires a deep understanding of design principles and manufacturing science.
China’s injection molding industry offers a mature ecosystem with cost-effective yet highly precise production options. Suppliers in regions like Dongguan, Shenzhen, and Suzhou are well-equipped to meet tight tolerance requirements for demanding industries like automotive, medical, and electronics.
By partnering with experienced Chinese manufacturers and applying best practices, businesses can achieve high-precision results without breaking the bank.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is tolerance in injection molding?
It refers to the permissible variation in a dimension from its nominal value. Tight tolerances ensure part consistency and functional compatibility.
Why is tolerance control important?
It ensures proper fit, function, and reliability in assembled products, especially for high-precision industries like medical, automotive, and electronics.
How tight can injection molding tolerances be?
With optimized tooling and process control, tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm are achievable in plastic injection molding.
What materials are best for tight tolerance molding?
Materials with low shrinkage and high dimensional stability such as PEEK, PC, and POM are preferred.
Are Chinese manufacturers reliable for tight tolerance molding?
Yes. Many Chinese molders have advanced equipment, quality control systems, and certifications like ISO13485, IATF16949 to support tight tolerance requirements.
How do I specify tolerances when working with a Chinese supplier?
Provide 2D drawings with GD&T annotations, highlight critical dimensions, and consult the supplier early in the DFM process.