1. Design and Engineering
The first step in plastic mold manufacturing is designing the mold using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Engineers create a 3D model of the mold, considering factors like material flow, cooling efficiency, and part ejection. The design must ensure precision to avoid defects in the final plastic product.
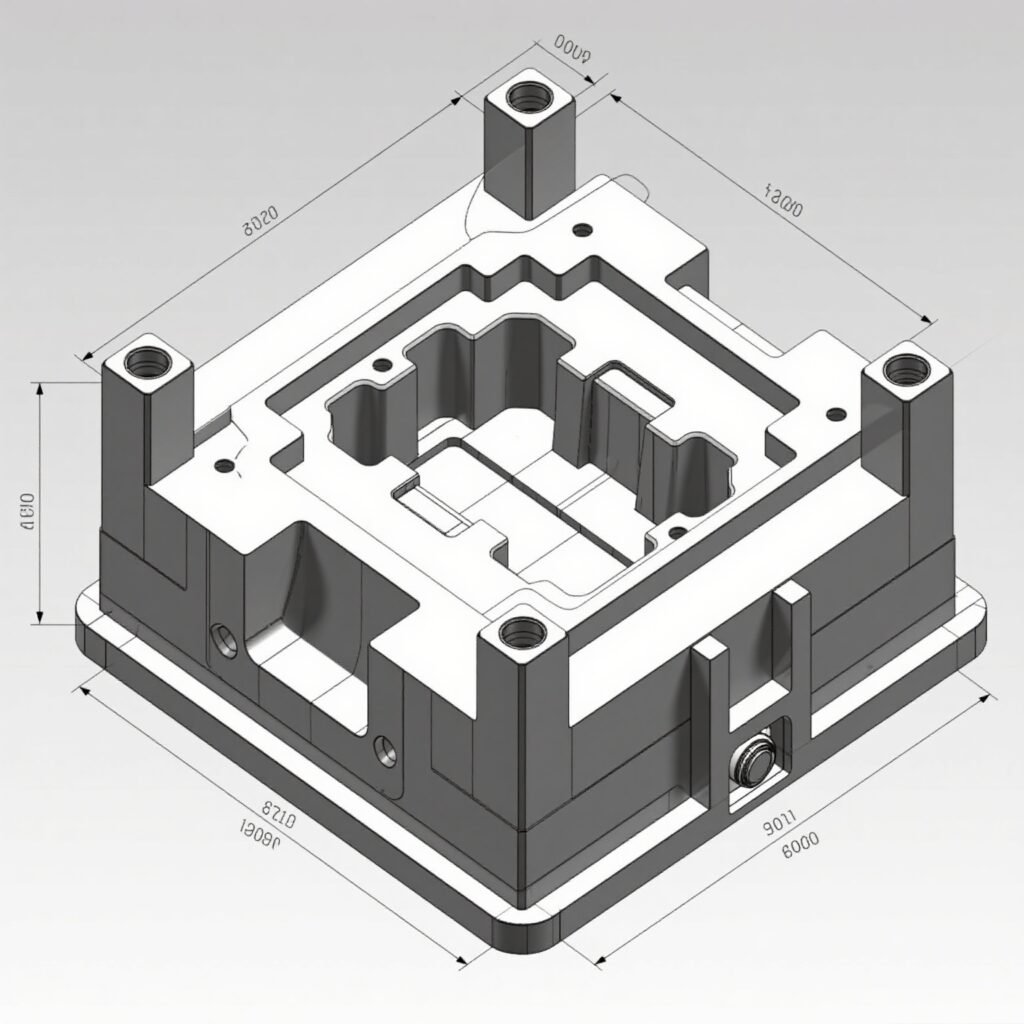
Image: CAD design of a plastic mold
2. Material Selection
The mold is typically made from hardened steel or aluminum, depending on production volume and cost requirements. Steel molds are durable and suitable for high-volume production, while aluminum molds are cheaper and faster to machine but wear out quicker.
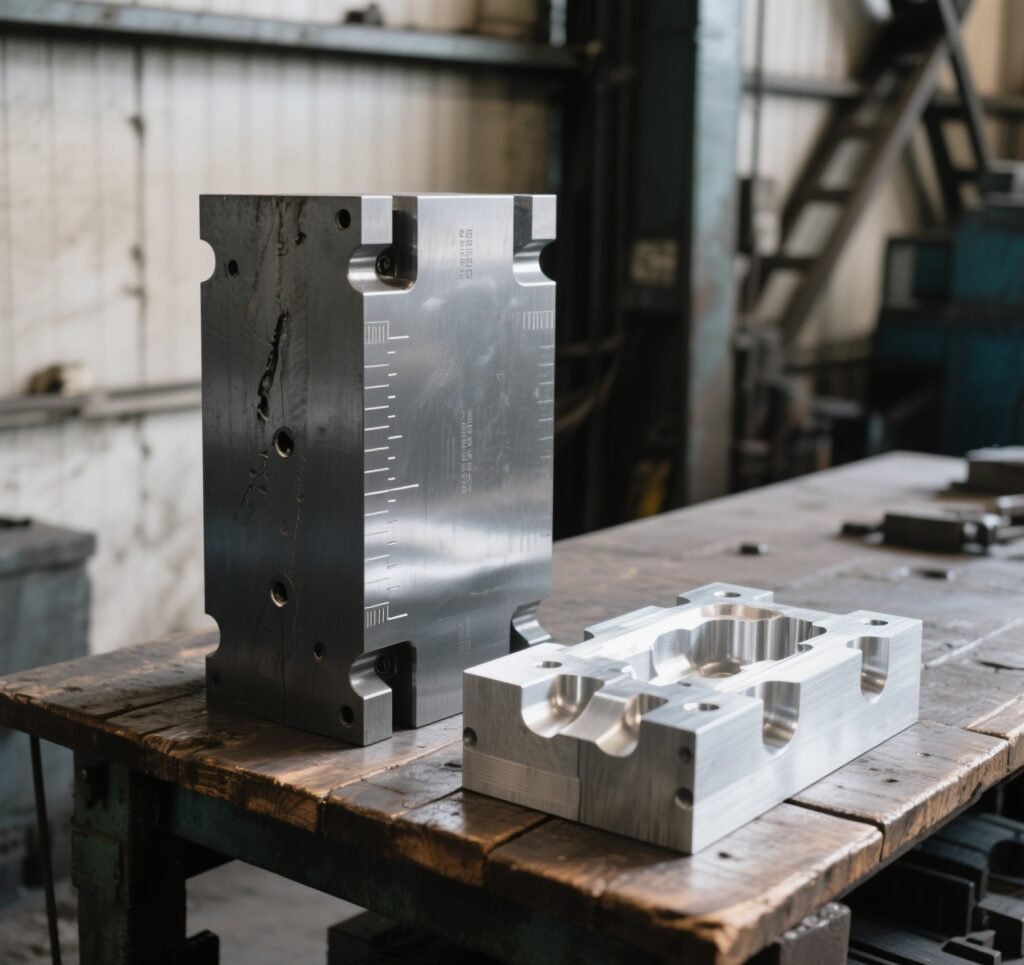

Image: Steel and aluminum mold blocks
3. CNC Machining
Once the design is finalized, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are used to precisely cut and shape the mold components. CNC milling, turning, and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) ensure high accuracy in creating cavities, cores, and ejector pins.
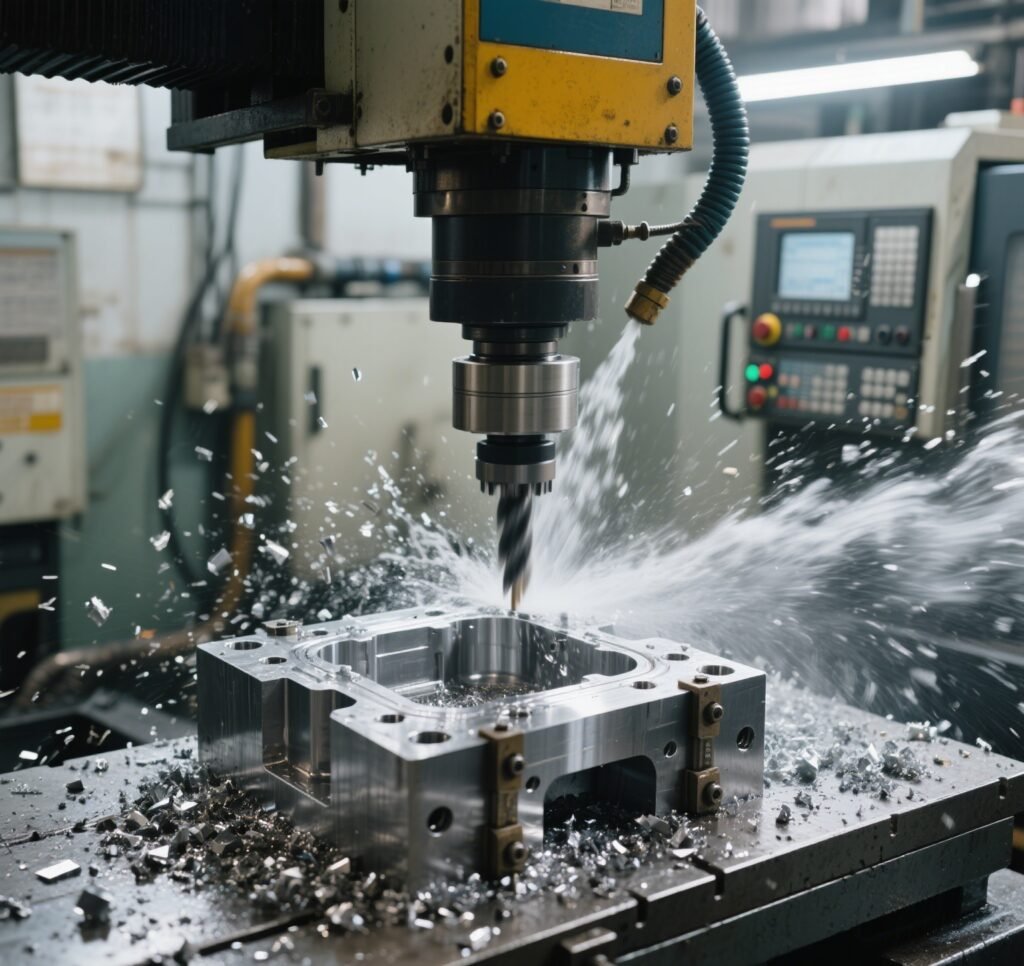

(Image: CNC machine cutting a mold cavity)
4. Heat Treatment (If Applicable)
For steel molds, heat treatment is often applied to enhance hardness and durability. Processes like quenching and tempering increase wear resistance, ensuring the mold withstands repeated injection cycles without deformation.
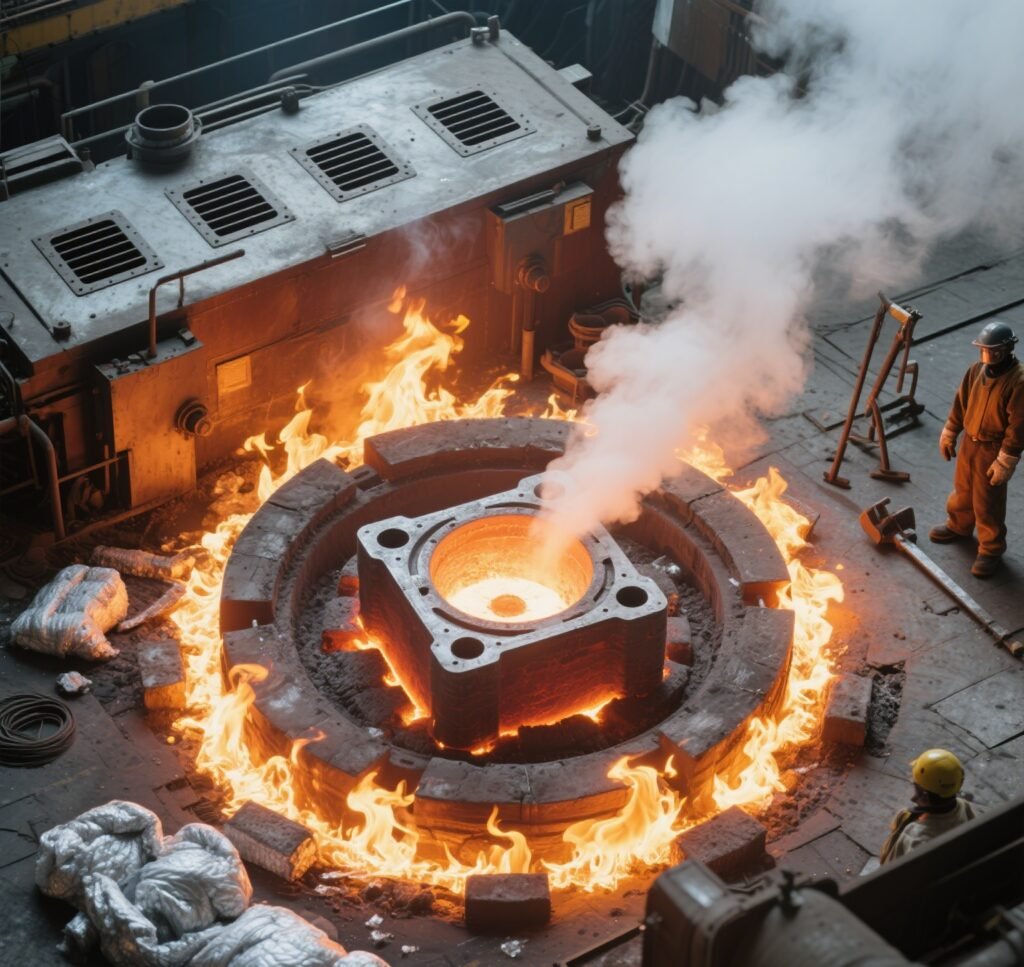

(Image: Mold undergoing heat treatment in a furnace)
5. Assembly and Fitting
After machining, all mold components—such as the core, cavity, ejector system, and cooling channels—are carefully assembled. Technicians ensure proper alignment and smooth movement to prevent defects in molded parts.
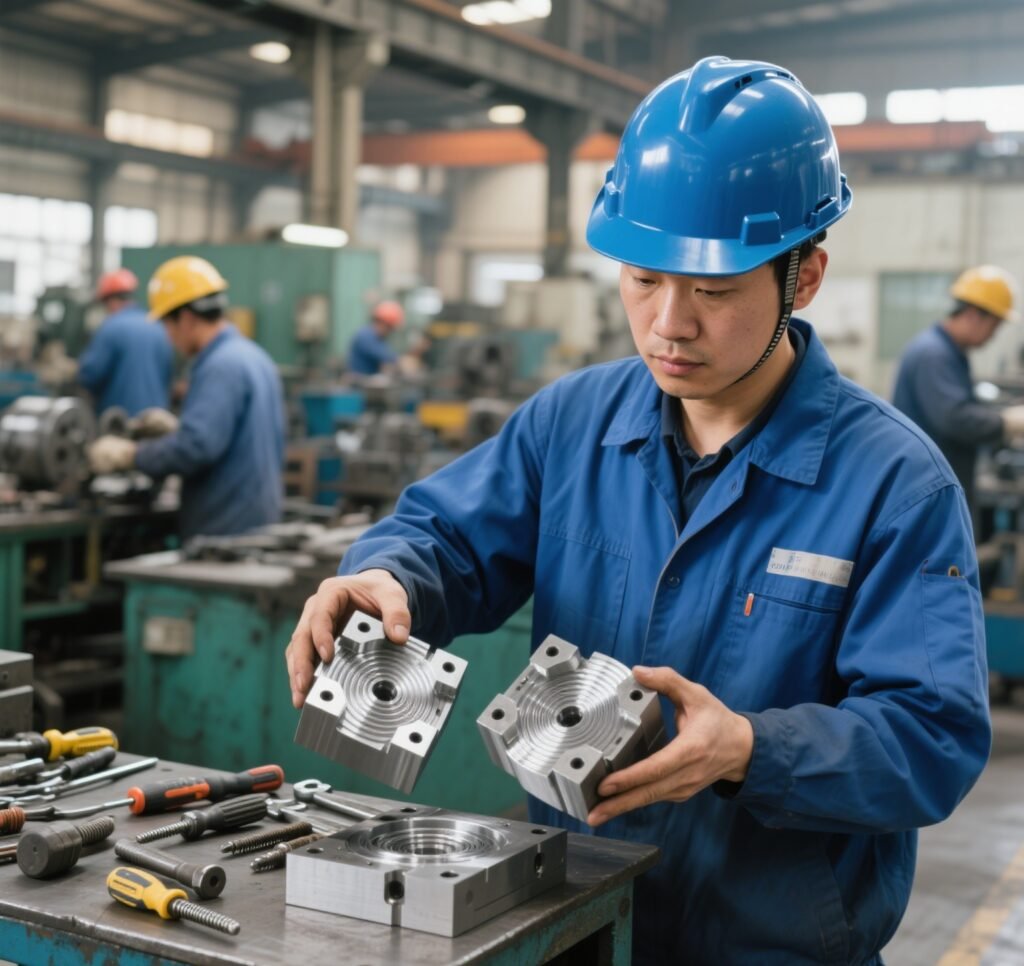

(Image: Worker assembling mold components)
6. Testing and Adjustments
The completed mold is tested in an injection molding machine to verify performance. Engineers check for issues like uneven filling, warping, or ejection problems. Adjustments are made to optimize cycle time and part quality.
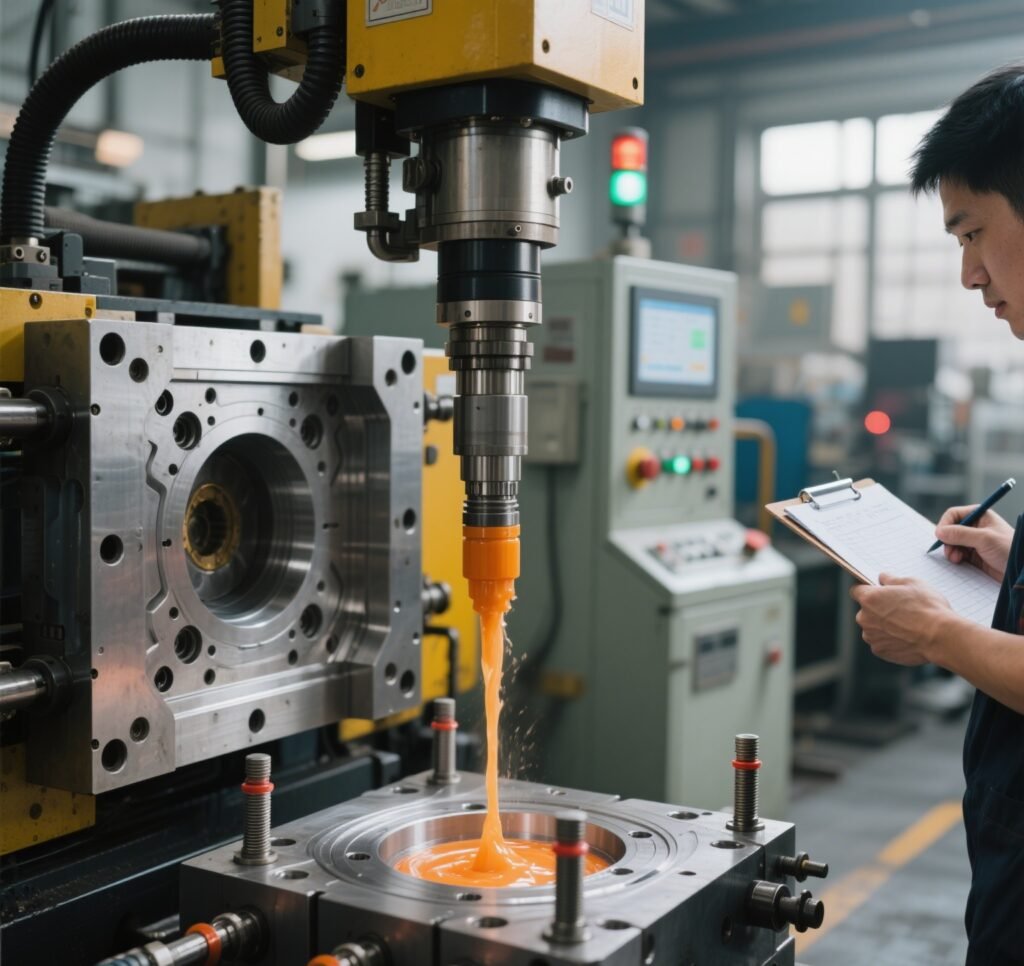

(Image: Injection molding machine testing a new mold)
7. Final Polishing and Finishing
The mold surface is polished to achieve the desired texture (glossy, matte, or textured). A smooth finish reduces friction during ejection and improves the appearance of plastic parts.
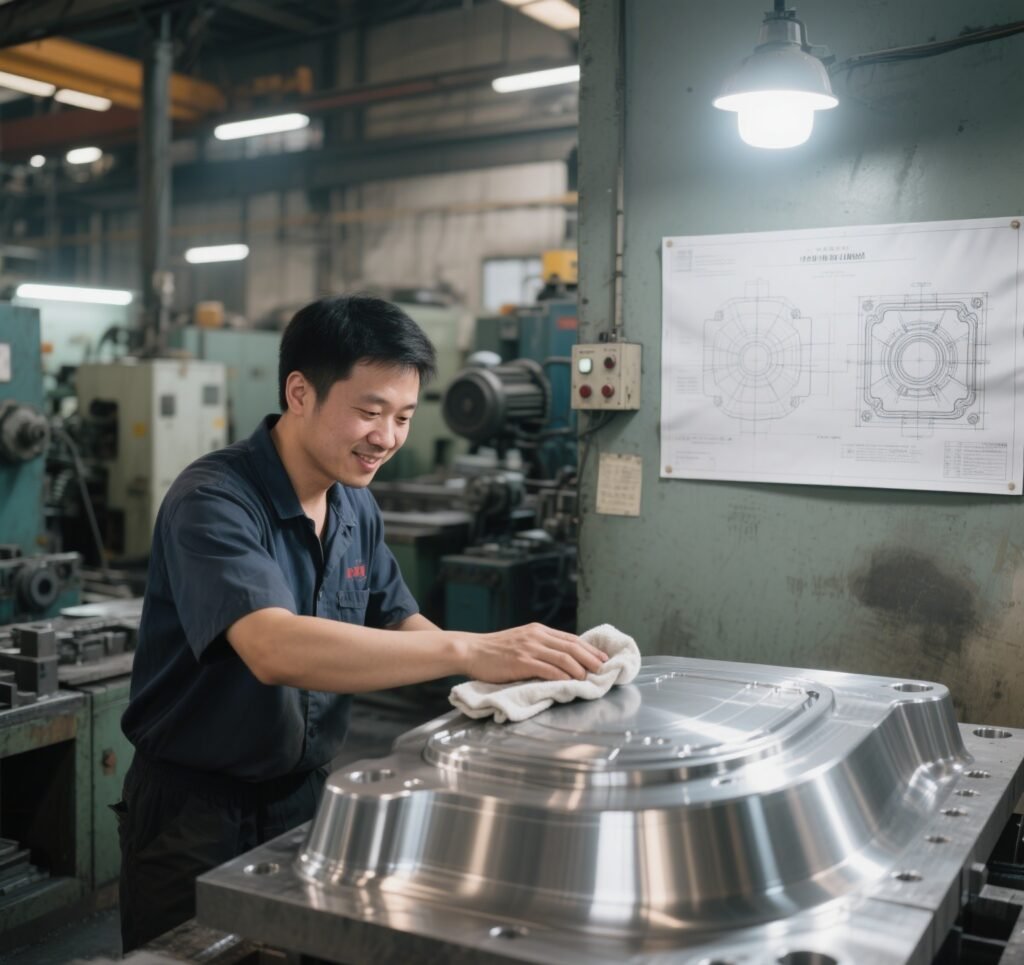

(Image: Technician polishing a mold surface)
8. Production and Maintenance
Once approved, the mold is used for mass production. Regular maintenance—cleaning, lubrication, and inspection—extends its lifespan and ensures consistent part quality.
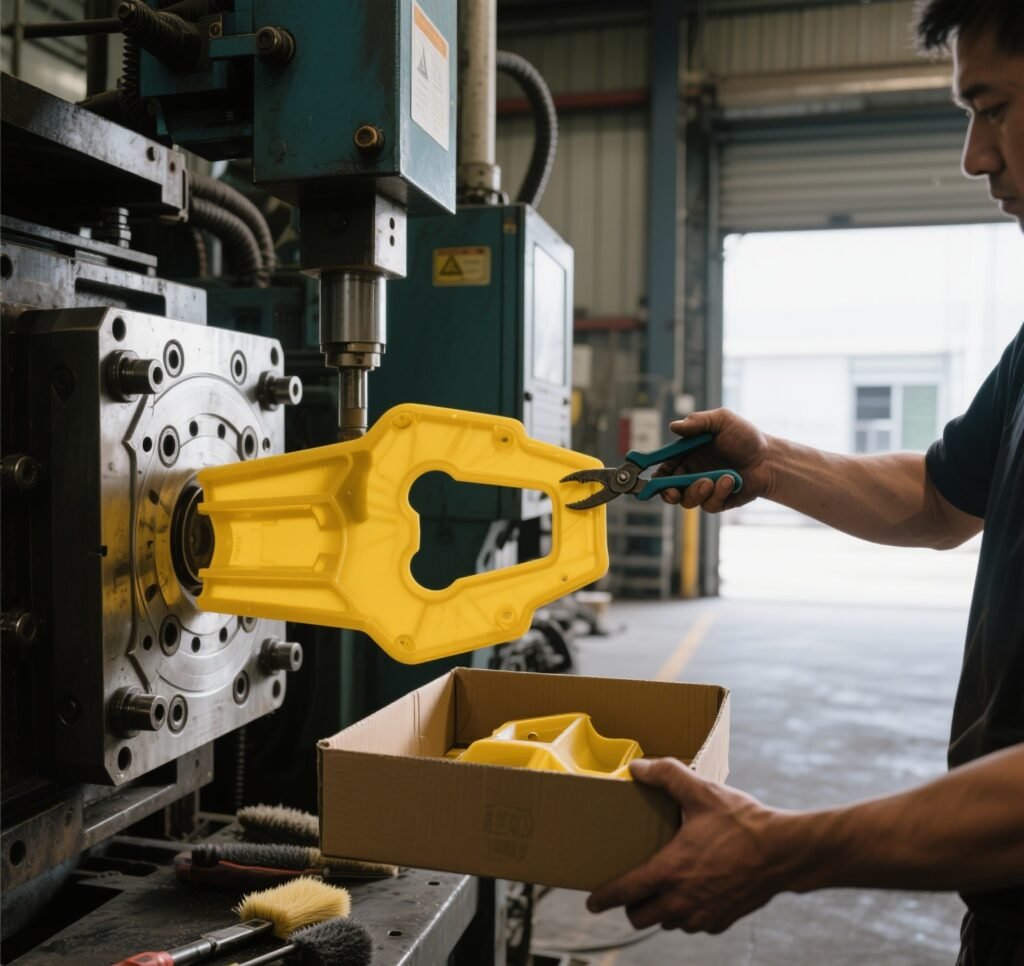

(Image: Plastic parts being ejected from a mold)
This structured process ensures high-quality plastic molds that meet industry standards for precision and durability.