An Article Describing the Key Technical Points of Plastic Molds
Need to get a handle on the key technical points of plastic molds? This article describing the key technical points of plastic molds dives into the types of molds, materials, design workflows, and common issues. You’ll get a thorough understanding to enhance your plastic molding projects. Additionally, consider reading an article describing the key technical points of plastic molds for more insights.
Key Takeaways
- Plastic molds are essential for producing a wide range of items with high precision, playing a critical role in various industries including healthcare and automotive.
- Material selection for molds, such as steel and aluminum, greatly affects production costs, durability, and suitability for specific manufacturing needs.
- Advancements in mold technology and automation improve efficiency, reduce defects, and enhance the overall quality control process in plastic molding, reaching a point where process efficiency and quality control are optimized.
What are Plastic Molds?
Integral to the plastic processing industry, plastic molds produce items with precise shapes and sizes, ensuring consistency and quality. Everyday items, from water bottles to automotive parts, are crafted using these molds.
As an example, a plastic bottle cap is commonly made using plastic molds to achieve uniformity and durability.
Precision in molding ensures the functionality of products. For medical devices or intricate electronic components, accuracy is paramount. Plastic molds are indispensable for achieving this precision across various industries.
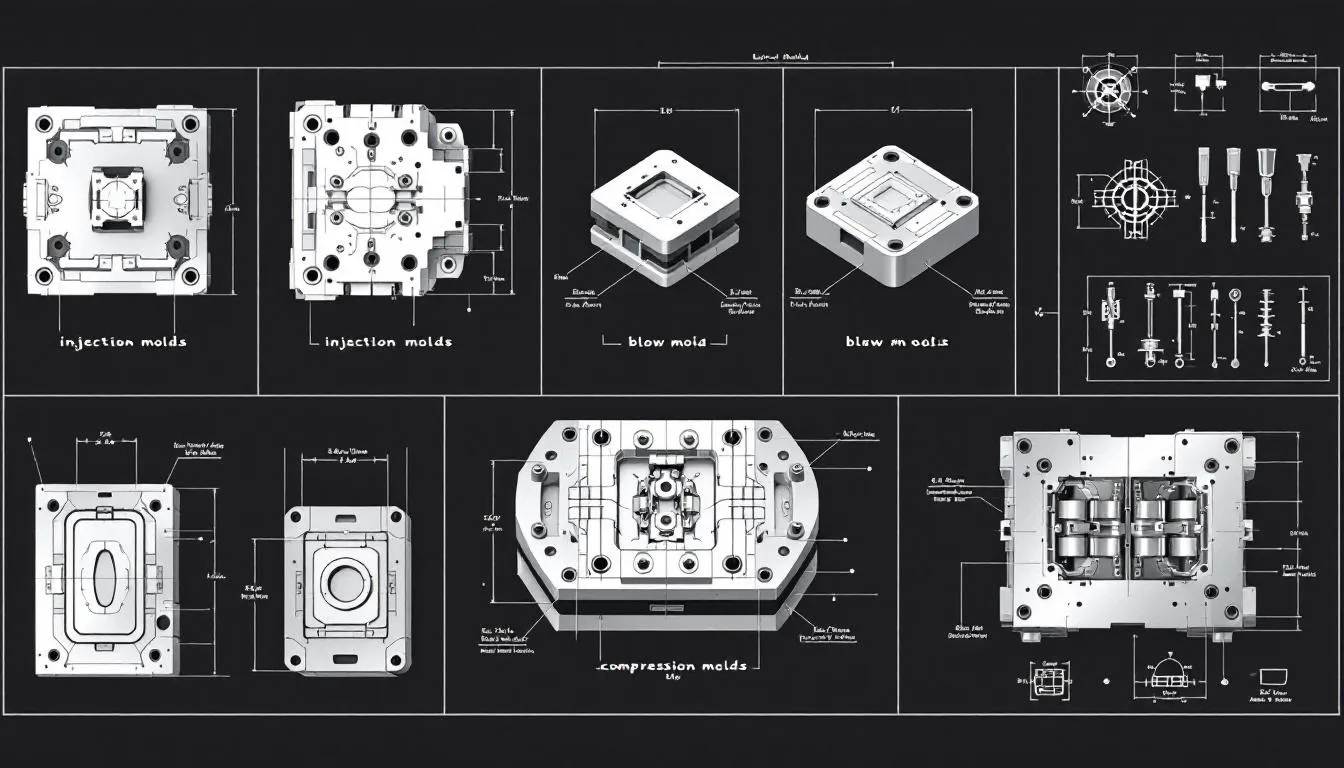
Types of Plastic Molds
Plastic molds are tailored to specific molding processes and come in various types. The main types include:
- Injection molds: widely used for high-volume production, ideal for creating complex, detailed parts quickly and efficiently.
- Blow molds
- Compression molds
Blow molds, on the other hand, are perfect for producing hollow objects like bottles. They work by inflating heated plastic into a mold cavity. Compression molds are suitable for manufacturing solid, thicker parts and are often used for items like large containers or automotive components, especially when compared to blow molds. Some compression molds are specifically designed to create multiple portions of a product in a single cycle, allowing for efficient separation and production of different parts.
Materials Used in Plastic Molds
Material selection for plastic molds significantly impacts functionality and durability. Key points about steel molds include:
- Due to their hardness, steel molds are ideal for producing detailed features and maintaining tight tolerances.
- They are perfect for high-volume production.
- The initial tooling cost for steel molds is higher.
Conversely, aluminum molds have the following characteristics:
- Lower initial tooling cost
- Easier to modify and repair
- Heat and cool faster than steel, making them suitable for low-volume production
- May wear out faster in high-stress applications
Recently, the industry has shifted towards eco-friendly materials. Biodegradable polymers are popular as manufacturers seek sustainable alternatives. Material choice influences cost, environmental impact, and production process effectiveness.
Additionally, alcohol is sometimes used as a cleaning agent for molds due to its effectiveness in removing residues.
The Mold Design Process
Designing a plastic mold begins with defining prototype objectives. This phase aligns design priorities with manufacturing capabilities. Next, 3D models are created, incorporating essential elements like parting lines and cooling channels.
The process involves:
- Simulations that identify potential issues before machining begins.
- Determining optimal melting flow and cooling rates to determine proper mold function.
- Using CNC technology to precisely cut mold components from metal blocks, adhering to design specifications.
Refinements and iterative evaluations adjust design and process parameters to meet specifications. Integrating 3D printing with injection molding facilitates rapid prototyping and customization, reducing lead times.
Mold Components and Accessories
Mold components and accessories are the backbone of any successful plastic molding process, much like how every word in a story shapes its meaning. The mold base serves as the sturdy foundation, typically crafted from robust materials such as steel or aluminum, ensuring the entire structure can withstand the heat and pressure of repeated cycles. Cavities are meticulously designed spaces where the plastic material is injected, forming the precise shape and size of the final product—each cavity is as vital to the process as a single word is to the overall word count in a well-written article.
Cores play a crucial role in creating holes or recesses within the molded part, allowing for complex geometries and functional features. Ejector pins, meanwhile, are responsible for the smooth removal of the finished product from the mold, preventing damage and ensuring a clean separation, much like the careful removal of unnecessary words can improve the clarity of a document.
To further enhance the molding process, accessories such as mold release agents are used to prevent the plastic from sticking to the mold, reducing the risk of a painful mess during removal. Temperature control systems are another essential accessory, regulating the mold’s temperature to ensure consistent material flow and optimal product quality. Just as removing Eddie Murphy’s voice from “A Thousand Words” would strip the film of its greatest comedic asset, neglecting these components and accessories can compromise the entire process, leading to defects and inefficiencies. By carefully selecting and maintaining these elements, manufacturers can ensure that every shot, every word, and every detail contributes to a high-quality final product.
Injection Molding Process
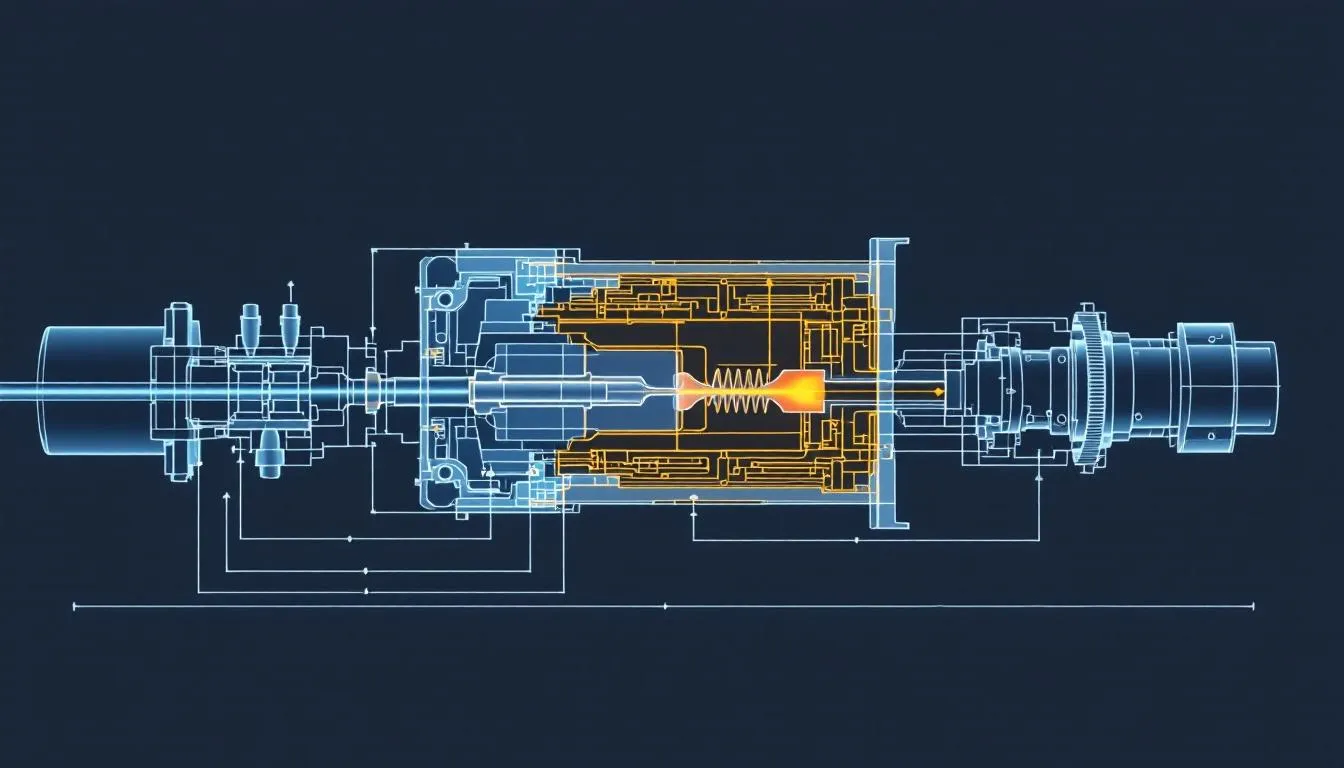
Injection molding involved injecting melted plastic into a mold under high pressure to create solid parts. This method is ideal for high-volume production of intricate designs. The process consists of five main stages:
- Clamping
- Injection
- Cooling
- Ejection
- Inspection
In the injection stage:
- Plastic granules are melted and forced into the mold cavity.
- Cooling time, which varies based on plastic type and part thickness, is crucial for final product quality.
- Proper temperature control prevents surface defects and delays in part ejection, ensuring that the injected product meets quality standards.
Robotic automation revolutionizes injection molding, enabling continuous production without human intervention. Regular machine calibration and process control maintain consistent quality and reduce defects like warping and material inconsistencies in the program, proving that a picture is worth a thousand words.
Key Technical Points in Plastic Molding
Plastic molds are complex, with systems for pouring, temperature regulation, and ejection, all critical for effective molding. The position of these systems within the mold is crucial, as proper placement ensures optimal flow, cooling, and ejection, directly impacting the quality of the molded product. Increasing mold temperatures and reducing reliance on mold-release agents prevent delamination caused by contaminants. Aluminum’s excellent heat dissipation helps reduce cycle times and defects.
Warping from uneven internal shrinkage during cooling is prevented by sufficient cooling time and uniform wall thickness. Flow lines, visible streaks on molded parts, are mitigated by adjusting injection speed and maintaining consistent wall thickness, which can lead to variation in the final product.
Weld lines, weakening a part’s structure, occur when two molten resin flows meet improperly. To avoid this issue and other defects:
- Optimize temperature and pressure during injection.
- Control injection pressure to minimize defects like jetting and sink marks.
- Ensure proper wall thickness to decrease defects.
Common Issues and Solutions in Plastic Molding
Production errors often cause common issues in plastic molding, affecting final product quality. A standard maintenance schedule for molds prevents frequent production errors and prolongs mold life. Recording maintenance details, such as inspection times and performed repairs, is essential to ensure effective issue prevention. Aluminum molds, easier to repair and modify than steel, offer a practical solution for production errors.
Proactively addressing these issues maintains high-quality standards and efficient production processes. Regular inspections and timely repairs significantly reduce downtime and enhance productivity.
Maintenance and Repair of Plastic Molds
Maintaining and repairing plastic molds is a process that demands attention to detail, much like tracking the word count and keyword density in a well-optimized article. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent issues such as wear, corrosion, or damage to critical components, ensuring that each mold continues to produce high-quality products throughout its lifespan. This routine care might involve cleaning the mold, inspecting for signs of damage, and replacing worn parts—each step as important as monitoring the reading level and grammar in a document to ensure clarity and effectiveness.
When repairs are needed, the process can range from simple component replacement to more complex refurbishments, such as restoring cavities or cores. In some cases, extensive damage may require a complete rebuild of the mold, which can be as time-consuming and costly as rewriting an entire story to meet a strict word limit. However, just as Jack in “A Thousand Words” learns the value of every word—each leaf that falls from his tree bringing him closer to his limit—manufacturers must recognize the importance of every maintenance action. Each word, each leaf, and each component counts toward the longevity and performance of the mold.
By implementing a proactive maintenance schedule and addressing repairs promptly, manufacturers can extend the life of their molds, reduce downtime, and maintain consistent product quality. This approach not only optimizes the process but also ensures that every word, every shot, and every product meets the highest standards—proving that attention to detail, whether in writing or manufacturing, makes all the difference.
Advances in Plastic Mold Technology
Recent advancements in plastic mold technology have revolutionized the industry. Energy-efficient injection molding machines reduce operational costs and minimize environmental impact. These innovations improve efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing processes.
Technological advancements drive the industry forward, with new materials and methods enhancing product quality and precision. Innovative combinations of materials and technologies are further optimizing product quality and precision. Automation and AI integration streamline production and improve quality control.
Cost Factors in Plastic Mold Production
Several factors influence plastic mold production costs. Aluminum is preferred for low-volume production due to its cost-effectiveness and quick heating and cooling. However, it may wear out after 10,000 cycles, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
Higher production volumes reduce cost per unit due to economies of scale, making it more financially efficient. The length of production runs can also impact overall cost efficiency, as longer runs often lead to lower costs per part. Cost estimation tools help manufacturers analyze cost drivers and optimize production processes.
Quality Control in Plastic Molding
Quality control in plastic injection molding involves a four-stage process:
- Design review
- Mold inspection
- In-process quality controls
- Final inspection
Quality checks during mold assembly ensure all components align correctly and function as intended.
Post-ejection quality control checks for defects like warping or sink marks, indicating needed adjustments in molding settings. AI and machine learning enhance quality control by predicting defects and improving process efficiency, as issues are detected early, leading to effective removal of the truth and maintaining an optimal track ratio.
Final inspections finally identify surface imperfections or tolerance issues, ensuring only high-quality products reach the customer.
Applications of Plastic Molds
Plastic molds are versatile tools used across various industries to produce a wide range of products. In healthcare, they craft precise medical devices like syringes and equipment housings. Advances in micro injection molding enable precise production of small components for electronics and medical devices.
The technology industry uses plastic molding for durable casings, internal components, and accessories for electronic devices. Aerospace applications use plastic molds to create lightweight yet strong components for aircraft and defense systems.
Additionally, plastic molding generally produced everyday items like food containers, utensils, and storage bins.
Summary
Throughout this exploration of plastic molds, we’ve delved into their types, materials, design process, and technical intricacies. Understanding these aspects is crucial for appreciating the role plastic molds play in manufacturing high-quality, precise products.
As we look to the future, advancements in technology and materials will continue to drive the industry forward, making plastic molding more efficient, sustainable, and versatile. Embracing these innovations will undoubtedly shape the next generation of manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are plastic molds?
Plastic molds are essential tools in the plastic processing industry, designed to produce items with precise shapes and sizes. Their accuracy ensures consistent quality in manufactured products.
What materials are commonly used for making plastic molds?
Steel and aluminum are the most commonly used materials for making plastic molds, valued for their durability and cost-effectiveness.
What are the main types of plastic molds?
The main types of plastic molds are injection molds, blow molds, and compression molds, each designed for particular applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate mold for your project.
How does the injection molding process work?
The injection molding process works by injecting melted plastic into a mold at high pressure, allowing it to cool before the solidified product is ejected. This efficient method produces precise and consistent shapes in manufacturing.
What are some common issues in plastic molding?
Common issues in plastic molding, such as warping, delamination, and sink marks, are frequently attributed to production errors and inconsistencies in materials. Addressing these factors is crucial for ensuring high-quality outcomes.